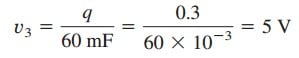This time we will learn about capacitors in series and parallel examples. This thing is crucial for us like learning the series and parallel resistors. We know from resistive circuits that a series-parallel combination is a powerful tool for reducing circuits.
This technique can be extended to series-parallel connections of capacitors, which are sometimes encountered.
Parallel Capacitors Formula
In order to obtain the equivalent capacitor Ceq of N capacitors in parallel, consider the circuit in Figure.(1a).

The equivalent circuit is in Figure.(1b). Note that the capacitors have the same voltage v across them. Applying KCL to Figure.(1a),

But ik = Ck dv/dt. Hence,

where

The equivalent capacitance of N parallel-connected capacitors is the
sum of the individual capacitances.
We observe that capacitors in parallel combine in the same manner as resistors in series.
Series Capacitors Formula
We now obtain Ceq of N capacitors connected in series by comparing the circuit in Figure.(2a) with the equivalent circuit in Figure.(2b).
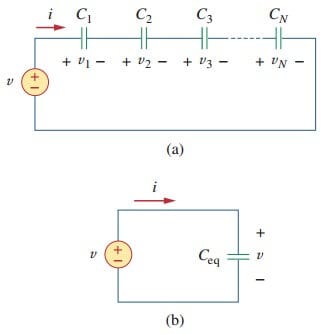
Note that the same current i flows (and consequently the same charge) through the capacitors. Applying KVL to the loop in Figure.(2a),

But,

Therefore,

where

The initial voltage v(t0) across Ceq is required by KVL to be the sum of
the capacitor voltages at t0. Or according to Equation.(5),
![]()
Thus, according to Equation.(6),
The equivalent capacitance of series-connected capacitors is the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual capacitances.
Note that capacitors in series combine in the same manner as resistors in parallel. For N = 2 (i.e., two capacitors in series), Equation.(6) becomes

Read also : 1K resistor color code
Capacitors in Series and Parallel Examples
1. Find the equivalent capacitance seen between terminals a and b of the circuit in Figure.(3).

Solution:
The 20- μF and 5- μF capacitors are in series; their equivalent capacitance is
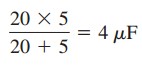
This 4- μF capacitor is in parallel with the 6- μF and 20- μF capacitors; their combined capacitance is
![]()
This 30- μF capacitor is in series with the 60- μF capacitor. Hence, the equivalent capacitance for the entire circuit is
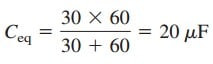
2. For the circuit in Figure.(4), find the voltage across each capacitor.

Solution:
We first find the equivalent capacitance Ceq, shown in Figure.(5). The two
parallel capacitors in Figure.(4) can be combined to get
40 + 20 = 60 mF.

This 60-mF capacitor is in series with the 20-mF and 30-mF capacitors. Thus,

The total charge is
![]() This is the charge on the 20-mF and 30-mF capacitors because they are in series with the 30-V source. (A crude way to see this is to imagine that charge acts like current, since i = dq/dt.) Therefore,
This is the charge on the 20-mF and 30-mF capacitors because they are in series with the 30-V source. (A crude way to see this is to imagine that charge acts like current, since i = dq/dt.) Therefore,
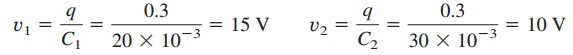 Having determined v1 and v2, we now use KVL to determine v3 by
Having determined v1 and v2, we now use KVL to determine v3 by
![]() Alternatively, since the 40-mF and 20-mF capacitors are in parallel, they have the same voltage v3 and their combined capacitance is
Alternatively, since the 40-mF and 20-mF capacitors are in parallel, they have the same voltage v3 and their combined capacitance is
40 + 20 = 60 mF.
This combined capacitance is in series with the 20-mF and 30-mF capacitors and consequently has the same charge on it. Hence,